
- Summary
- Before You Begin: Understanding The Complexity of Market Engagement
- Overview: A Step-by-Step Guide to Building Your B2B GTM Framework
- Step 1. Define Your Objectives and Target Market
- Step 2. Craft a Compelling Value Proposition
- Step 3: Set a Pricing Model That Reflects Value
- Step 4. Ensure Cross-Functional Team Alignment
- Step 5. Choose the Right Marketing Channels
- Step 6. Outline a Sales Strategy and Customer Journey
- Step 7. Set the key performance metrics (KPIs) and targets that define success
- A Note on ROI and Stakeholder Buy-In
- Implementing an ROI-Tracking System
- Have O8 Build Your Go-to-Market Strategy
A go-to-market (GTM) strategy is a comprehensive action plan that defines how your company will reach and engage with customers, delivering your unique value proposition to the marketplace effectively. Whether you’re launching a new product, entering a new market, rebranding, or updating your offerings, a strategic GTM approach is essential to ensure your initiative meets its goals.
Before You Begin: Understanding The Complexity of Market Engagement
Embarking on any significant market initiative without a clear GTM strategy can lead to disjointed efforts and misallocated resources. The strategic absence can hinder your business's ability to effectively engage with the market and achieve sustainable growth.
Navigating the Complexities
As we delve into constructing a GTM strategy, it’s important to recognize the broad application and crucial impact of this plan. This broader view ensures that we address specific needs tailored to varying business scenarios.
Common Roadblocks:
- Misaligned Market Entry: Whether entering a new market or launching a new product, failing to align your business model with market demands can result in low adoption and poor market penetration.
- Incoherent Messaging: Without a cohesive messaging strategy that resonates with the intended audience, your brand risks being misunderstood or ignored, diminishing the impact of your marketing efforts.
- Pricing Missteps: Setting the wrong price for your product or service, especially without considering the competitive landscape and customer expectations, can severely limit your market entry or growth.
- Lack of Internal Alignment: A GTM strategy requires collaboration across multiple departments. Without it, you might face inconsistent customer experiences and inefficient resource use.
- Inadequate Metrics for Success: Without establishing clear KPIs, businesses struggle to measure the effectiveness of their GTM strategy, missing opportunities for optimization and refinement.
Overview: A Step-by-Step Guide to Building Your B2B GTM Framework
While these steps don't necessarily need to be done in order, they constitute the components of a successful B2B GTM strategy:
- Step 1: Define Your Objectives and Target Market: Clearly state what you aim to achieve with your GTM strategy and identify who your target customers are. This could include new demographics, existing customers, or users in a new geographical location.
- Step 2: Craft a Compelling Value Proposition: Articulate what makes your offering unique and why it should matter to your target audience. This proposition should be the cornerstone of all your communications.
- Step 3: Set a Pricing Model That Reflects Value: Develop a pricing strategy that not only considers cost but also the perceived value, competitive positioning, and customer willingness to pay.
- Step 4: Ensure Cross-Functional Team Alignment: Align your marketing, sales, product, and customer support teams around the GTM strategy to ensure consistent messaging and seamless customer experience.
- Step 5: Select Optimal Marketing and Sales Channels: Identify the most effective channels to reach your target audience. This might include digital marketing, direct sales, partnerships, or traditional advertising.
- Step 6: Outline a Sales Strategy and Customer Journey: Map out how customers will move from awareness to purchase and beyond. This includes defining the sales funnel, key touchpoints, and conversion strategies.
- Step 7: Implement Metrics and Analytics: Establish KPIs to measure the effectiveness of each element of your GTM strategy. Regularly review these metrics to adapt and refine your approach.
A dynamic and well-planned GTM strategy is pivotal for any business initiative’s success. We delve into each of these below.
Step 1. Define Your Objectives and Target Market
When embarking on a new business initiative, the clarity of your goals and a deep understanding of your target market are essential. This step is about more than just who you will sell to; it’s about precisely aligning every aspect of your GTM strategy to the specific needs and behaviors of your audience, setting a clear direction for your entire organization.
Setting Clear Objectives

Start by defining what you want to achieve with your GTM strategy. Objectives should be specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART). These could range from increasing market share, generating a certain revenue amount within a specific period, enhancing brand awareness in a new market, or successfully launching a new product or feature. Each goal should directly support your broader business strategy and provide a clear benchmark for success.
Examples of SMART objectives:
- Increase market share by 15% in the European market by Q4 2024.
- Achieve $2 million in revenue from the new product line within the first year of launch.
- Grow brand awareness in the Asian market by 25% as measured by customer surveys and social media engagement by the end of 2024.
Identifying Your Target Market
Understanding your target market is pivotal. This involves not just knowing who your customers are but also understanding their needs, preferences, decision-making processes, and how they prefer to interact with your brand.
- Demographic and Psychographic Segmentation: Begin by segmenting your market demographically (age, gender, income, education level, etc.) and psychographically (values, interests, lifestyles). This data helps tailor your messaging and product offerings to match the specific characteristics and behaviors of your segments.
- Geographical Considerations: If your GTM strategy involves entering new geographical areas, consider local cultural nuances, language differences, and economic conditions. Local market research is invaluable here, providing insights into regional consumer behavior and potential barriers to entry.
- Existing vs. New Customers: Determine whether your strategy focuses on deepening engagement with existing customers or acquiring new ones. For existing markets, leverage data on customer satisfaction and past purchasing behaviors. For new markets, use market analysis to identify potential customers and their needs.
- Buyer Personas: Develop detailed buyer personas that represent typical customers within your target market. These personas should include job roles, industry specifics, daily challenges, personal aspirations, and the buyer’s journey. This helps create more targeted and effective marketing messages.
- Use of Market Research Tools: Utilize tools and methods like surveys, focus groups, and market segmentation analysis to gather and validate information about your target market. Data analytics can also uncover trends and patterns in customer behavior that are critical for refining your strategy.
Example:
Suppose a SaaS company is launching a project management tool specifically designed for remote teams. The company’s objectives might include capturing 10% of the remote work tools market within two years. For the target market, they would focus on tech companies with distributed teams, identify key decision-makers like IT managers and team leads, and build personas around these roles, focusing on their need for seamless collaboration and efficient workflow management.
By defining clear objectives and deeply understanding your target market, you lay a solid foundation for your GTM strategy. This not only guides your product development and marketing efforts but also ensures that every action taken aligns with what your target customers need and value. This alignment is crucial for achieving the outcomes you’ve set for your business initiative.
More On Buyer Personas and Ideal Customer Profiles:
An ideal customer profile (ICP) describes the characteristics of a prospect or customer who would benefit most from your product or service. It serves as a single source of truth, delineating traits, preferences, and needs. It also informs essential elements in your business model like pricing strategy, sales strategy, target marketing, etc.
Marketing without clearly understanding who you aim to attract is like shooting in the dark. You might hit a few metric improvements that still fall short of your business goals.
If it hasn't clicked for you yet, our interactions with clients tell us this "drill" example can provide some clarity. Imagine you sell drills. Most potential customers don't want to hear about its speed, colors, or handle material. They don't want a drill at all. Instead, they care about making a hole, putting a screw in, and hanging their family photo. Hanging a family photo is their actual desire. Here, it's clear that the most effective marketing strategies focus on what your ideal customer profile truly wants to accomplish rather than what you are trying to sell.
In theory, you could remember to reference your target audience's needs, traits, and preferences without a document. But, looking back into your marketing campaigns, are they all aligned to a unified goal, offering what your customers need? Likely not, and that's fine; it's only human to let details sometimes fall through the cracks. To this end, the goal of a living persona document is to minimize and eliminate the chances you forget about what drives your customers and prospects, so every campaign has the foundation to be profitable.

Sample O8 Buyer Persona
Include quantitative and qualitative data into your personas to make them comprehensive:
- Quantitative data tells you the "what" and gives you a broad market overview.
- Qualitative data reveals the "why" behind your customers' actions and helps you understand their motivations and needs.
A Case Study
Both types of data give you a complete understanding of your target customers, which is why we gathered them for a medical SaaS client.
One of the activities we did on the qualitative front was to talk to the sales team, those interacting with customers and prospects daily. These interviews clarified marketing messages that persuaded prospects to book a demo, the consequences to their personal lives that they’d face if they didn’t solve their problem, and competitors’ solutions that they are also considering.
We then looked at external data that backed or refuted our findings:
- The U.S. Census Bureau is where we gathered that most of our client’s customers were middle-class health professionals who identified as female.
- SparkToro, a consumer analytics tool, then validated our assumptions around our core demographic information, media consumption, and interests.
- LinkedIn, where we searched for real-life examples of healthcare professionals who fit the profile to see how they talk, who they engage with, and the types of publications they read.
Based on these insights, we crafted an ICP for our client. We can’t share it for privacy reasons, but it detailed the story of a healthcare professional in their mid-30s to late 50s who owns or operates a small clinic or private practice in urban or suburban areas. With this knowledge, we went on to produce marketing messages that truly persuaded new customers to buy, exactly as you would.
Step 2. Craft a Compelling Value Proposition
Creating a compelling value proposition is foundational to the success of your go-to-market (GTM) strategy. It articulates the essence of what makes your product or service unique and explains why it should matter to your target audience. A strong value proposition acts as the cornerstone of all your communications, guiding the messaging across marketing, sales, and even customer support. Here’s how you can craft a value proposition that resonates deeply with your audience and distinguishes your offering from the competition.
Identify Your Unique Selling Points
Start by identifying what sets your product or service apart from the competition. Consider the features, benefits, or experiences that are unique to your offering. Ask yourself:
- What does my product do that no other product can?
- What problem does my product solve uniquely well?
- How is my solution better or different from existing alternatives?
Understand Your Target Audience
A value proposition should be tailored to the specific needs, desires, and pain points of your target audience. Conduct market research, gather customer feedback, and develop detailed buyer personas to understand your audience deeply. This understanding will ensure that your value proposition is not just clear and concise but also highly relevant to the people you aim to serve.
- What drives your customers’ decisions?
- What are their primary challenges or pain points?
- What benefits do they value the most?
Articulate the Benefits Clearly
The most effective value propositions go beyond just listing product features—they articulate the benefits in a way that resonates with the target audience. Your value proposition should clearly explain how your product improves your customers’ lives or solves their problems. Use simple, jargon-free language to convey:
- The immediate benefit to the customer.
- How it delivers on a deeper level (e.g., time savings, cost reduction, increased efficiency, peace of mind).
Differentiate From the Competition
Highlight how your offering is different from or better than what's available on the market. This might involve innovation, additional features, better customer service, or a more compelling overall experience. Clearly articulating this differentiation will help your target audience understand why they should choose you over others.
Consistency Across All Touchpoints
Once you have crafted your value proposition, integrate it consistently across all communication touchpoints. Whether it’s your website, social media channels, advertising, product packaging, or customer service scripts, the core message should be unmistakable and echo through all channels.
Example of a Strong Value Proposition:
Suppose you are a company offering a cloud-based project management tool. Your value proposition might be: "Streamline your team's workflow with our all-in-one project management solution that saves time, reduces costs, and enhances collaboration, enabling you to deliver projects faster and more efficiently than ever." This statement isn't very refined as far as the copy goes, but you'll note that it directly addresses common pain points like project delays, high costs, and team disorganization while highlighting the unique benefit of an integrated solution.
Validate and Refine
Test your value proposition with a segment of your target audience to gauge its impact. Collect feedback and be prepared to refine your statement to better align with customer perceptions and needs. This iterative process will help you hone a value proposition that not only captures attention but also convincingly communicates the unique value of your offering.
By crafting a clear and compelling value proposition, you set a strong foundation for your GTM strategy. It serves as a crucial guidepost for all your marketing and sales efforts, ensuring that every piece of content you create and every interaction you have with customers reinforces the unique benefits of your solution. This not only aids in attracting and converting leads but also in building long-term customer loyalty.
Step 3: Set a Pricing Model That Reflects Value

Pricing is more than just a number—it’s a pivotal part of your go-to-market strategy that communicates your product's value to the market, affects customer perception, and plays a crucial role in positioning within the competitive landscape. Developing a pricing strategy that reflects the true value of your offering requires a thoughtful balance between cost, perceived value, competitive factors, and what your customers are actually willing to pay.
Understanding Cost-Based Pricing
Begin with a cost-based analysis, ensuring that the price of your product covers the cost of production, including both direct costs like materials and indirect costs like overhead. This is your baseline, ensuring that no matter what, your pricing covers expenses and maintains a profit margin.
Leveraging Value-Based Pricing
Value-based pricing goes beyond mere costs and sets prices primarily on the perceived value to the customer. This method aligns pricing with the benefits your product provides, such as time savings, cost reductions, increased efficiency, or other improvements in the customer’s life or business.
- Identify Key Benefits: Focus on the most compelling benefits your product offers and quantify them if possible. For example, if your software saves an average of 10 hours per week for a team member, translate that time into monetary savings based on average wage costs.
- Research Willingness to Pay: Use customer surveys, interviews, and market tests to gauge how much customers value these benefits and what they are willing to pay for them.
Consider Competitive Positioning
Your pricing strategy should also consider the broader market and competitive landscape. Research how similar products are priced and positioned:
- Benchmark Against Competitors: Identify pricing tiers in your market segment. Are most competitors targeting a premium space, or are they competing on low cost?
- Differentiate: If your product offers unique features or superior performance, pricing can reflect this. Conversely, if entering a crowded market, you might need to meet or slightly undercut competitors to gain entry.
Dynamic Pricing Strategies
Adopt dynamic pricing models that allow flexibility based on market conditions, customer segments, or purchase behaviors:
- Tiered Pricing: Offer different pricing levels that correspond to varying levels of functionality or service. This can cater to different segments of your market based on their size, needs, or budget.
- Volume Discounts: Encourage larger purchases or longer subscription commitments by offering discounts. This can help lock in revenue upfront and increase customer lifetime value.
- Promotional Pricing: Temporarily reducing prices can accelerate market entry or boost sales during slow periods. However, use this tactic sparingly to avoid undermining perceived value.
Communicating Your Pricing Effectively
How you communicate your pricing can influence its perception:
- Transparent Pricing: Clearly explain what customers are paying for and ensure there are no hidden costs. This builds trust and aligns expectations.
- Highlight Value: Always connect your pricing back to the value proposition. Remind customers of the benefits and ROI they can expect from your product.
An Example:
For a SaaS company offering project management tools, a tiered pricing model could be effective. The base tier might include essential features suitable for small teams, priced competitively to attract startups and small businesses. Higher tiers could add advanced features like automation and integration capabilities, aimed at larger enterprises willing to pay a premium for increased efficiency.
Setting a pricing model that reflects the true value of your product requires a deep understanding of your costs, customer perceptions, and competitive dynamics. By aligning your pricing strategy with these factors, you can effectively position your product in the market, attract your target audience, and achieve your business goals.
Step 4. Ensure Cross-Functional Team Alignment
In any go-to-market (GTM) strategy, the alignment of cross-functional teams—marketing, sales, product, and customer support—is crucial. This synergy ensures that everyone is on the same page, which in turn, leads to consistent messaging and a seamless customer experience. Here’s how to align these key areas effectively to maximize the impact of your GTM efforts.
Establish a Unified Vision
The first step in aligning cross-functional teams is to establish a clear, unified vision of what the GTM strategy aims to achieve. This includes understanding the target market, the problem the product solves, and the unique value proposition. Ensure every team understands not only their role but how it contributes to the overall business objectives.
- Strategic Workshops: Conduct workshops that bring leaders and key team members from each function together to discuss and define the GTM strategy.
- Shared Goals and KPIs: Set common goals and key performance indicators (KPIs) that encourage collaboration and collective accountability.
Create Communication Channels
Effective communication is the backbone of cross-functional alignment. Without it, teams can easily become siloed, leading to inconsistent customer experiences and inefficiencies.
- Regular Cross-Functional Meetings: Hold regular meetings where teams can update each other on progress, discuss challenges, and synchronize efforts.
- Centralized Information Hub: Use a shared platform where updates, documents, and feedback can be accessed by all relevant teams, ensuring everyone has the most current information.
Align on Customer Messaging
Consistent messaging across all touchpoints creates a cohesive brand experience that can significantly enhance customer trust and loyalty.
- Unified Messaging Document: Develop a master document that outlines key messaging, tone, and communication guidelines. This document should be accessible to everyone involved in communication efforts.
- Review Processes: Implement regular reviews of outbound materials by representatives from each team to ensure all communications are on-brand and aligned with the strategic objectives.
Integrate Customer Feedback
Integrating feedback from customer-facing teams back into the product and marketing strategy can dramatically improve product offerings and customer communications.
- Feedback Loops: Establish mechanisms for customer support and sales teams to provide feedback directly to product and marketing teams. This could include regular feedback sessions, shared reports, or digital forums.
- Customer Insights Sharing: Make customer insights available to all teams. This can help product teams prioritize features or fixes, assist marketing in adjusting campaign strategies, and enable sales teams to understand customer sentiments.
Coordinate Go-To-Market Activities
Ensure that all GTM activities are well-coordinated between teams. This synchronization helps in delivering a seamless customer journey from awareness through purchase and beyond.
- Launch Planning: Coordinate launch activities across teams to ensure that marketing campaigns, sales readiness, and support capabilities are all activated simultaneously and cohesively.
- Role Clarification: Clearly define the roles and responsibilities of each team during each phase of the GTM strategy to avoid overlap and ensure coverage across all customer touchpoints.
An Example:
Imagine a technology company launching a new software product. The marketing team develops the core messaging and initial campaigns, sales teams are trained on the product’s features and ideal customer profiles, the product team continues to iterate based on beta testing feedback, and customer support is briefed on common issues and resolution paths. Regular alignment meetings ensure each team is aware of the latest developments and strategies are adjusted based on collective insights.
By ensuring that marketing, sales, product, and customer support teams are aligned around the GTM strategy, organizations can deliver a more consistent and effective customer experience. This not only improves efficiency and cohesion internally but also enhances customer satisfaction and loyalty, driving better business outcomes.
How to Align on Customer Messaging
A messaging document encapsulates phrases, unique value propositions, and stories that help you have a customer-first mindset regarding writing and content development.
This means putting yourself in the shoes of your ICP and assessing what messages or content they need to hear at each phase of their journey to progress forward. Having a well-defined messaging document also helps maintain consistency in what you say, how you say it, and why you say it.
Scattered or misaligned messages can confuse customers looking to buy your product or service, as they need clarity, not conflicting information about your business.
You can use a message house as your guiding single source of truth for your team to align. It's the framework we use at O8 because it's simple to explain, understand, and brief, helping both sales and marketing departments stay on the same page.
A message house typically has three or more parts and can be expanded upon if needed. As the foundation, it should have the following components:
- The WHY - The roof holds the main message that all your communications should align with. This is often your company's most compelling value proposition, mission, or purpose. Use the following structure as guidance: "We exist to [make something better/solve a common problem/overcome obstacles]."
- The HOW and WHAT - Three or more columns with messages that support your main message. These messages should highlight how you do what you do differently and better than everyone else.
- The WHO - A foundation of data that supports other social proof, statistics, examples, and testimonials. People should read this data and know why your product or service is an excellent choice for them.
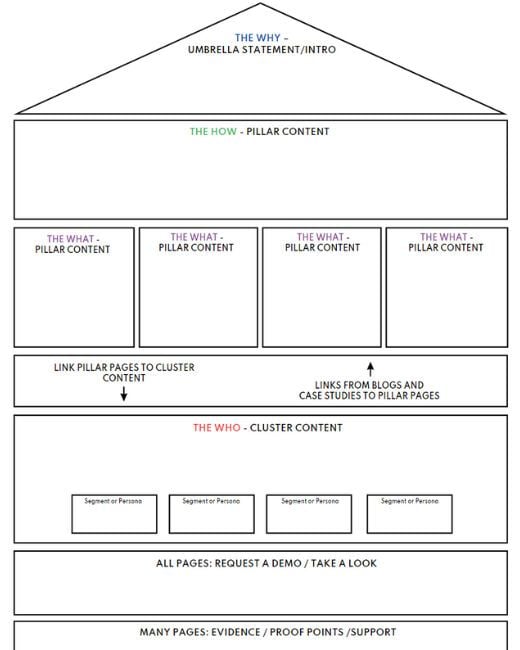
Example of a comprehensive O8 message house
Our message houses include more detail than the message house's creator intended. We like to dig deeper, specifying messages that resonate with subsets of our audience to address more niche service offerings.
You don't need this level of detail to benefit from a message house. Let's take the example of a message house that Mark Fest, the creator of the message house, presented in his free e-book.

It’s for the New Americans Campaign, “a coalition of service providers aiming to modernize and streamline the delivery of naturalization assistance to legal permanent residents in the United States.”
You can easily create a Message House using the free Message House Toolkit's templates.
Step 5. Choose the Right Marketing Channels
Selecting the right marketing channels is pivotal to the success of your go-to-market (GTM) strategy. The effectiveness of these channels in reaching your target audience can greatly influence the overall impact of your marketing efforts and the speed at which you achieve your business objectives. Here’s how to strategically choose the marketing channels that will best connect with your audience and drive results.
Assess Your Audience
Before deciding on the channels, you need a thorough understanding of your audience, including where they spend their time and how they prefer to consume information. This might involve:
- Market Research: Utilize surveys, industry reports, and analytics to gather insights into the media habits of your target demographics.
- Customer Interviews: Direct conversations with current or potential customers can yield valuable insights into their media consumption habits and preferences.
Evaluate Channel Effectiveness
Each marketing channel has its strengths and may appeal to different segments of your audience. Here’s a breakdown of common channels and how they might fit into your B2B marketing strategy:
- Content Marketing: By creating and distributing valuable, relevant, and consistent content, you can attract and engage a clearly-defined audience. Blogs, white papers, e-books, and case studies can establish your brand as a thought leader in your industry.
- Social Media: Platforms like LinkedIn are particularly effective for B2B marketing, providing opportunities to connect directly with decision-makers and influencers within industries. Twitter and Facebook can also be useful for engaging in industry conversations and boosting brand visibility.
- Email Campaigns: Email allows for direct and personalized communication with your audience. Segment your email list to tailor messages to different user groups based on their needs and your relationship with them.
- Targeted Online Advertising: PPC (pay-per-click) and display ads can be highly effective in reaching a targeted audience, especially when combined with retargeting strategies that keep your brand visible to visitors after they leave your site.
Align Channels with Your Sales Funnel
Each stage of your sales funnel might benefit from different channels:
- Awareness Stage: Use broad-reaching tools like social media and content marketing to generate brand awareness. Educational content works well here.
- Consideration Stage: Email campaigns and targeted advertising can nurture potential leads by providing more detailed information about your product or services.
- Decision Stage: Direct interaction through personalized emails, advanced content offers, or consultations can help convert prospects into customers.
Monitor and Optimize
After selecting your channels, continuously monitor their performance and impact. Use metrics such as engagement rates, conversion rates, and ROI to assess effectiveness:
- Analytics Tools: Utilize tools like Google Analytics, CRM software, and social media insights to track how different channels and content types perform.
- Feedback Loops: Implement systems to gather feedback from sales and customer service teams on the quality of leads and customer inquiries generated from different channels.
An Example:
Consider a SaaS company targeting mid-sized businesses. They might find LinkedIn an ideal platform for connecting with other business professionals, whereas detailed white papers and case studies shared through targeted email campaigns could help educate their audience about the product’s benefits and differentiate from competitors.
Choosing the right marketing channels is not just about spreading your message; it’s about crafting an approach that is tailored to the habits, preferences, and needs of your target audience. By carefully selecting and optimizing these channels, you can ensure that your GTM strategy is not only seen but also resonates with those who are most likely to benefit from your offering, ultimately driving engagement and sales.
More on Defining Your Marketing Channels
Different channels can attract different audiences and subsets of people at different times for diverse reasons. For example, TikTok is often more attractive and engaging for teenagers than for senior adults. So what if you need a platform to sell fitness apps to upper-middle-class women between 29 and 38 looking to lose ten pounds? The more precise you focus the lens, the more complex the targeting can become.
Your gut feeling can take you to a certain point of confidence, especially if you’ve built it from successful marketing campaigns. However, it can also blind you to other avenues or channels where your ICPs spend time and energy.
For example, Emerson, our client, needed help finding workers for their factory. They considered using LinkedIn Ads, as they had experience with the platform. Our analysis revealed that the target individuals spent considerably more time on Meta not LinkedIn. We also learned that there was urgency attached to the project, meaning that long-term activities such as in-depth content development weren’t an option. The proposition, calls to action, and implementation had to be clear and concise.
While we could have found some of the workers on LinkedIn’s Ad platform, they frequented Meta more, making Facebook a more effective channel
We referenced the demographic information provided by our client to construct audiences in Meta ads for the type of applicants they needed. Creative assets were reviewed with productive discussions, which led to the correct details and CTAs. We were confident that the ad impressions would persuade ICPs to apply, including our client’s competitive pay, signing bonus, and flexible working hours. We launched Meta Ads (Facebook and Instagram) in various formats to entice people to consider our client for employment.
Multiple hiring campaigns spanning multiple weeks (and sometimes months) were placed through Meta. Through these campaigns and other tactics deployed by the client (particularly billboards), suitable candidates began applying for the positions. Importantly, the multiple campaigns (some using video, others using static imagery) helped us and our client learn what worked best for this type of recruitment.
Subsequent campaign review discussions with experts at Meta validated our methods and gave us additional thoughts for future campaigns. We, of course, were delighted that our clients reported favorably about the inflow of candidates to hire.
While the problem may not be hiring competent talent, the approach remains the same. You need to find a customer base that fits a specific description and resonates with certain messages. If you’ve followed our tips so far, you should have this information in a customer profile and messaging document.
If you don’t know where your customers are, or there’s a disconnect between where your customers said they spend their time and where they do, fear not! You can start multiple low-scale campaigns, gather data, and double down on the most profitable platforms.
Step 6. Outline a Sales Strategy and Customer Journey
Developing a structured sales strategy and mapping out the customer journey are critical steps in your go-to-market (GTM) strategy. These elements help you visualize how potential customers move from initial awareness of your product or service to making a purchase and eventually becoming brand advocates. By defining the sales funnel, identifying key touchpoints, and implementing effective conversion strategies, you can create a smooth and compelling journey for your customers. Here’s how to approach this vital task.
Define the Sales Funnel

The sales funnel provides a framework for understanding the stages customers go through before deciding to purchase. Typically, this funnel includes several key phases:
- Awareness: Potential customers become aware of your solution through various channels such as social media, content marketing, or advertising.
- Interest: At this stage, prospects are actively looking for solutions to their problems and begin to engage more deeply with your content, perhaps subscribing to a newsletter or following social media channels.
- Consideration: Prospects are evaluating your offering against competitors. They might engage in trials, read customer testimonials, or interact with sales representatives.
- Decision: The final purchasing decision is made. Effective sales support and clear value communication are crucial here.
- Retention: After purchase, the focus shifts to keeping customers satisfied with excellent service and ongoing engagement, encouraging repeat business.
- Advocacy: Satisfied customers become brand advocates, spreading the word to others and potentially driving more organic growth.
Identify Key Touchpoints
Each stage of your sales funnel should have specific touchpoints where you engage with the customer. These are opportunities to influence their journey:
- Awareness: SEO-optimized blog posts, engaging videos, industry articles, and targeted ads.
- Interest: Interactive webinars, detailed e-books, informative newsletters, and engaging social media posts.
- Consideration: Product demos, comprehensive case studies, customer testimonials, and personalized consultations.
- Decision: Tailored offers, clear and simple pricing structures, and streamlined purchasing processes.
- Retention: Regular follow-up emails, customer support, user communities, and loyalty programs.
- Advocacy: Referral incentives, social proof through testimonials, and features on community successes.
Develop Conversion Strategies
Effective conversion strategies are tailored to move prospects to the next stage of the funnel efficiently:
- Content Personalization: Tailor content to meet the specific needs and interests of prospects at each stage. Use data-driven insights to customize messages and offers.
- Engagement Tactics: Implement engagement tactics such as live chats, FAQs, and active social media engagement to answer queries and overcome objections in real time.
- Follow-Up Strategies: Use email marketing and retargeting ads to remind prospects of your offerings and bring them back to your site to continue their journey.
- Sales Enablement: Equip your sales team with the right tools and information—such as updated data sheets, presentation materials, and training on the latest product enhancements—to help them close deals effectively.
Monitor and Optimize
Continuously monitor the effectiveness of each touchpoint and strategy within your sales funnel through analytics and customer feedback. Use this data to refine your approach, addressing bottlenecks and optimizing the journey to improve conversion rates and customer satisfaction.
An Example:
Imagine a B2B software company that offers customer relationship management tools. The sales funnel might look like this:
- Awareness: The company uses targeted LinkedIn ads to reach potential customers.
- Interest: Interested prospects might attend a webinar that demonstrates how the software can streamline their sales processes.
- Consideration: The prospect participates in a free trial, exploring the tool’s features with guidance from an assigned sales rep.
- Decision: The sales team presents a customized proposal based on the prospect’s usage during the trial.
- Retention: The company offers ongoing training sessions and updates about new features to current customers.
- Advocacy: Satisfied customers are encouraged to share their positive experiences on social media in exchange for additional features or discounts.
By meticulously outlining your sales strategy and customer journey, you ensure that your GTM efforts are not only strategic but also aligned with the expectations and behaviors of your target market. This alignment helps in building stronger relationships with customers, enhancing their satisfaction, and ultimately, boosting your company’s growth and reputation in the market.
More On Customer Journey Mapping
A "customer journey" depicts the touchpoints and steps an average prospect encounters on the road to becoming customers, fans, and brand advocates—like a roadmap. Prospects who fall under the same ideal customer profile have different pain points depending on their stage in the journey. Jumping straight into marketing execution without a journey map can leave gaps where customers might fall out of their path to conversion. You also increase the risk of overinvesting in a message or effort that doesn't fit their stage or level of awareness.
Here's a case in point: GenoPalate, a direct-to-consumer brand, approached O8 because it routinely achieved high website traffic but low conversion rates. While mapping their customer journey, we discovered that prospects learning about GenoPalate through its website were upper-middle-class women looking to lose ten pounds. They needed straightforward, actionable guidance, not overly complicated, and deeply clinical scientific information.
We created distinct landing pages for their different customer profiles. Some of these pages were aimed at website visitors who didn't know about GenoPalate at all, while others targeted people with at least some familiarity with their brand.
The customer journey was designed to begin from the homepage. Visitors were immediately asked to choose their primary interests (such as weight loss, improved fitness, disease management, etc.) from a drop-down menu prominently displayed in the homepage feature area. Once visitors arrived at the resulting landing page, they could download distinct e-books that enrolled them into unique email sequences.
Here's a look at our concept prior to design and development:

By mapping the customer journey and implementing personalized UX and messaging strategies, GenoPalate saw a significant lift in their conversion rates. Here, the implementation of personalized landing pages was the most meaningful next step toward relevancy for their distinct customer segments.
To map your customer journey, ask yourself questions like:
- What channels or sources did they use to discover us?
- Were there any specific incentives or factors that tipped the scale?
- What ultimately led the customer to choose our product or service?
- How did the customer first become aware of our existing products or services?
- What specific information did the customer look for during their research?
- Did they encounter any difficulties or obstacles during the purchasing process?
As with customer profiles, conversations with those client-facing roles directly interacting with customers will help you map your buyer’s journey. For more data-backed insights, you can also lean on tools indicating how users interact with your current marketing channels.
For example, Hotjar is a widget you can install on your website that records privacy-protected use recordings. You can witness how people scroll, click, and navigate your site’s pages. Hotjar also generates heat maps on demand. You can see how far visitors scroll down a page, what sections or elements they click on, and what they ignore.
Hotjar in use
These direct visuals and context clues complement data from Google Analytics and Google Search Console. As you acquire a more complete picture of the customer journey through your website, this information is what aids business decision-makers in making real strategic decisions rather than acting on assumptions.
Optimizing Your User Experience
You often have as little as 50 milliseconds to make an impression on your ideal customers. Making your website experience as easy and hassle-free as possible is crucial.
Your challenge is that 96% of unhappy customers don’t voice complaints. Given how these people at least have a relationship with you, we believe the number of unhappy prospects that remain silent is just as high or worse.
These realities leave you with two challenges.
First, optimizing your user experience (UX) is critical to close sales. By ensuring a seamless and enjoyable process for your potential customers, you can significantly increase your chances of converting them into paying customers. Optimizing your customer experience involves making every touch point as intuitive, engaging, and rewarding as possible:
- Information architecture: Create clear navigation menus, intuitive categorization, and effective search functionalities so users can easily find the information they need and accomplish their tasks efficiently. A well-structured website architecture also helps search engines easily find and index information on your site, resulting in improved search rankings.
- Visual design: Pay attention to typography, colors, spacing, and imagery to create a cohesive and aesthetically pleasing experience. Align the visual design with your brand identity to reinforce brand recognition and evoke positive emotions.
- Optimize website performance: Users expect fast load times and seamless interactions. Perform rigorous testing to identify and fix any performance issues hindering the user experience.
Second, prospects and customers won’t always tell you what they like or don’t like. It’s up to you to create hypotheses around what could be going wrong, gather data to test the hypotheses and correct the course. For example, we like to use Hotjar to playback the exact page sessions from our website. We aim to check if the website structure we designed is as simple to navigate as we expected.
To get started, identify the critical components that will make a significant difference. This could include key user flows, core functionalities, or high-traffic areas of the website. By concentrating your efforts on these areas, you can optimize the most important aspects of the user experience. Address these pressing challenges before moving on to lower-priority improvements.
Step 7. Set the key performance metrics (KPIs) and targets that define success
To ensure the effectiveness of your go-to-market (GTM) strategy, it's crucial to implement a robust system of metrics and analytics. Establishing key performance indicators (KPIs) allows you to measure the success of each element of your strategy, from marketing efforts to sales execution. Regular review and analysis of these metrics enable you to adapt and refine your approach, ensuring continuous improvement and alignment with business objectives. Here’s how to effectively implement and utilize metrics and analytics in your GTM strategy.
Identify Relevant KPIs
Start by identifying the KPIs that are most relevant to your GTM strategy. These should be closely aligned with your business goals and provide clear indicators of success or areas needing improvement. Common KPIs for a GTM strategy might include:
- Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC): The total cost of acquiring a new customer, including all marketing and sales expenses.
- Lifetime Value (LTV): The total revenue a business can expect from a single customer throughout their relationship.
- Conversion Rates: The percentage of prospects who move from one stage of the sales funnel to the next.
- Retention Rates: The percentage of customers who remain with your company over a given period.
- Engagement Metrics: Measures of how actively engaged your audience is with your marketing materials, such as click-through rates, engagement rates on social media, and email open rates.
- Lead Generation Volume and Quality: The number of leads generated and how well they fit your ideal customer profile.
Set Up Tracking Systems
Implementing the right tools and systems to track these KPIs is critical. This might include:
- CRM Software: Tools like Salesforce or HubSpot can track sales interactions, customer relationships, and conversion rates.
- Analytics Platforms: Google Analytics and other web analytics tools can measure website traffic, user behavior, and engagement with your content.
- Marketing Automation Tools: These can help track lead generation and qualification, email marketing metrics, and campaign performance.
Regularly Review and Analyze Data
Regular data review sessions are essential for understanding the effectiveness of your GTM strategy. Schedule periodic meetings with key stakeholders to discuss these metrics:
- Monthly Reviews: Look at short-term performance indicators to adjust tactics quickly and respond to immediate challenges or opportunities.
- Quarterly Business Reviews: Assess longer-term trends and the impact of your GTM strategy on overall business goals. Adjust strategies as needed based on these insights.
Use Data to Inform Decisions
Data from your KPIs should directly inform decision-making processes:
- Optimize Campaigns: Use engagement and conversion data to tweak marketing campaigns, refine messaging, and better target your audience.
- Adjust Sales Strategies: Analyze sales cycle lengths, win rates, and feedback from sales interactions to refine your sales approach and training.
- Improve Product Offerings: Customer feedback and usage data can guide product development and feature prioritization.
An Example:
A tech startup may track the CAC and LTV to understand their spending efficiency in relation to long-term revenue generation per customer. If the CAC is too high relative to LTV, they might need to refine their marketing strategies, perhaps by focusing more on higher-converting channels or more cost-effective lead generation tactics.
By establishing and regularly reviewing relevant KPIs, you create a feedback loop that continually informs and refines your GTM strategy. This data-driven approach not only helps in achieving your immediate marketing and sales objectives but also aligns your long-term business strategy with actual market conditions and customer behaviors, ensuring sustainable growth and competitiveness in your industry.
More On KPIs
Before diving further into this topic, let’s explain the difference between “targets” and KPIs.” Targets are the specific goals you want to reach: the outcome you expect to achieve due to your efforts. KPIs (Key Performance Indicators) are the specific measurements used to assess the performance of business activities (such as a digital display ad campaign, for example). In other words, KPIs inform you of whether you’re likely to achieve your targets (or not).
For example, let's say you've set a target of increasing website traffic by 20% in the next quarter. The KPIs associated with this target could be metrics like website visits, unique visitors, or page views.
KPIs align team members on what the finish line looks like. Your marketing efforts avoid becoming fragmented and disjointed because your team has a shared understanding of business priorities and whether or not achieving the associated targets is on track.
Think of it this way: KPIs in service of your targets help avoid duplicate work, conflicting strategies, and wasted resources. Instead of acting like a group of people rowing a boat in different directions and going in circles, you're all rowing in the same direction with a common destination in mind.
Tracking KPIs helps not only your immediate team. You can provide senior executives with incremental snapshots and forecasts. You can have fact-formed discussions among your team and with leaders about actions to be taken if the successful achievement of a target is at risk.
Sometimes, targets might even be reset due to what the data tells you. This is a game changer for marketers and executives. KPIs are based on what's really happening. Without this information, vanity metrics like blog post output can take away your attention from your initial goal, such as generating inbound leads.
How do you start with KPIs?
Begin developing a KPI document by analyzing the results of past successful marketing campaigns. Here’s an example of a template:
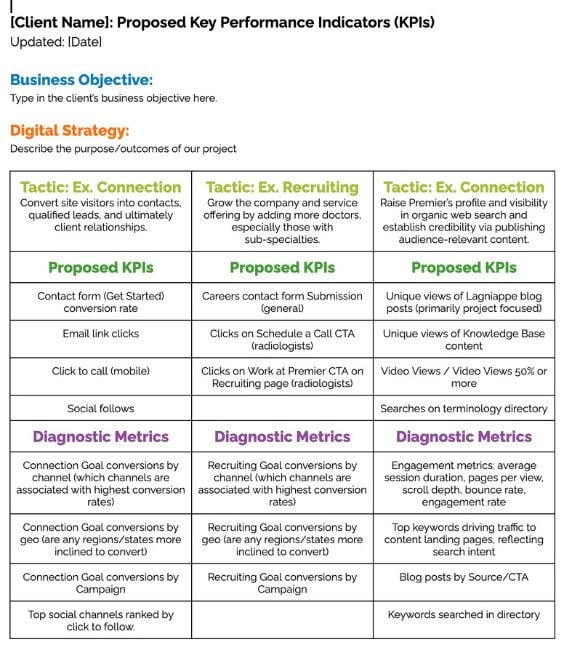
Use the data you already have to understand what's realistically achievable. If you don't have existing data, look for industry benchmarks or review other internal data that might give you clues, such as checking your project management tool to verify how long it takes to write a blog article or publish a new landing page.
Look for trends, patterns, and benchmarks to set your targets. For example, suppose you're focusing on increasing organic website traffic through SEO efforts. In that case, you might target a 10% or 20% quarter-over-quarter growth in site traffic based on industry standards or previous performance. This percent increase is your KPI for web traffic.
Where can you find data to set targets and KPIs?
If you’ve never set targets or are new to tracking data, an easy way to start is by looking at website data coming from Google Analytics, Google Search Console, and your content management system (CMS). Chances are you can access at least one of these tools to find data such as web form submission counts, retention rates, demo requests, or e-books downloaded.
Our encouragement to you is simple: You have to start somewhere, and you’ll improve your ability to set targets and KPIs over time. Resetting targets and KPIs as your new analysis habits take hold is common.
Finally, an important caveat: Remember that other business realities can affect your ability to achieve the projected results. Factors like adverse weather, economic downturns, new competitive entries, and many others can influence business outcomes.
A Note on ROI and Stakeholder Buy-In
At O8, we always keep this phrase from strategy advisor Chris Brogan in mind during every client engagement: "My favorite metric is the one with a dollar sign in front of it." While your CMO might enjoy the nuances of your go-to-market plan, most executives will half-listen until you provide an ROI (Return on Investment) number.
Projected ROI helps leaders compare their investment options and feel more confident about putting resources into their new product or service. It also signals you're serious about delivering real, measurable results.
Calculating ROI can be tricky because you need to consider all the costs and outcomes involved. For example, you spend $20,000 on ads to make $100,000. It looks like you made five times what you spent. But it's much less after including other costs, such as the marketing team who ran the ads and the sales teams who spoke with prospects.
To get a more accurate ROI, look at all the contributing factors like ad spend, customer acquisition costs, other expenses like employee salaries, and the total revenue generated. Altogether, this gives you a more accurate understanding of whether your marketing investment was profitable.
All our strategic projects include an ROI projection stage. We follow certain principles to make this information actionable and digestible:
- Keep it simple: Use clear and easy-to-understand language. Make sure the information flows logically and isn't overwhelming.
- Use visuals: Include charts, graphs, or pictures to help stakeholders visualize the projections and make the information more immediately understandable.
- Show the benefits: Highlight the positive outcomes the project will deliver. Use numbers to demonstrate how it will increase revenue, save costs, or improve customer satisfaction.
- Address risks: Talk about potential challenges or risks that could affect the projections. Explain your plans to overcome them and assure stakeholders that you've considered these factors.
- Align with their goals: Connect the projections to the stakeholders' priorities and interests. Show how the project supports their strategic objectives or solves their problems.
These projections convey a compelling case for the project's potential returns and align stakeholders' expectations with the anticipated outcomes. If you can effectively communicate the projected ROI, you'll increase the likelihood of gaining stakeholder buy-in and support for your initiatives.
Implementing an ROI-Tracking System
An ROI-tracking system such as HubSpot can really help prove the value of a go-to-market strategy and bring peace of mind to stakeholders. The marketing channels you chose in the steps above determine how you’ll report on your investment’s profit.
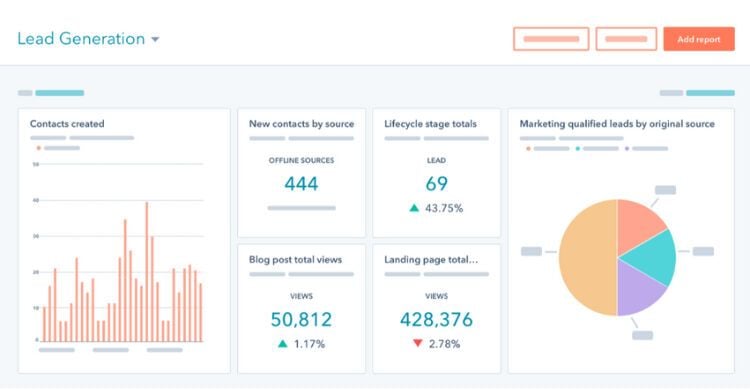
Sample Inbound Lead Generation Dashboard
Paid advertising platforms (such as Meta, Google, and LinkedIn) are incentivized to show detailed ROI reports because they need to demonstrate their worth to advertisers. If you can see and interpret the reporting, you can reliably share this information with stakeholders. It becomes easier to decide whether investing in specific initiatives and the associated channels is a good idea. That’s why these platforms make ROI information available.
Inbound campaigns are harder to measure. For example, there’s no straightforward method to track customers who saw a billboard of your brand seven months ago and bought a product today. You could ask them how they learned about you during their buying journey. Some companies don’t reliably do this because adding too many steps to the sales process can demotivate prospects from buying.
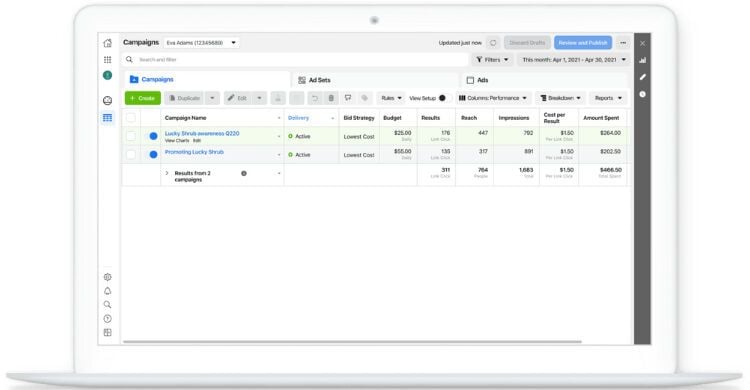
Meta’s Ad Manager
Still, we suggest regularly analyzing the data from your ROI-tracking system. Look for trends, patterns, and areas that need improvement. This information will guide you in refining your marketing approach, optimizing your campaigns, and making smart decisions based on data to achieve better results.
Have O8 Build Your Go-to-Market Strategy
O8’s team comprises marketing industry veterans with VP, directive, and other senior executive positions at B2B companies like yours. We’ve used go-to-market strategies to grow companies during budget cuts, layoffs, pressing needs, unclear priorities, and all the unideal situations you might be going through.
If you want to work with an agency that lives and breathes GTM, gives you the number to build a case for any project, and won’t tie you into inflexible contracts and bloated deliverables, book a free growth strategy call with us.







